You know about on-page SEO and off-page SEO – maybe you thought you knew it all! But now that Google is trying to answer as many user queries as possible on the search engine results page (SERP), there is one more type of SEO that you need to understand: on-SERP SEO. We briefly mentioned it in our last post – Is Google Hogging Your Search Traffic? – as something worth looking into because it’s expected to soar in popularity in the years to come as more and more marketers aim to take advantage of zero-click searches. So let’s dig in and explore this new frontier! Search results are evolving, and you don’t want to be left in the dust while your competitors surge ahead.

The Fight for Position 0
Google’s purported goal has always been to help users find what they’re looking for online. In the past, the search engine accomplished this by placing the most relevant, helpful website at the top of the results page (which was then the #1 spot of the organic listings). Now, they’re trying to present a satisfying answer on the SERP so that no further effort is necessary from the user – not even a single click of the mouse! The answer is provided above the search results – in the prime area known as “position 0” – or to the side of the search results.
More and more searches are now zero-click searches: 34.4 percent of desktop searches and 62.5 percent of mobile searches (source). Sometimes the information is presented as a knowledge panel, which is an automatically generated information-filled box that relies on Google’s Knowledge Graph. Other times, you’ll see a featured snippet, which is a selection of text from a webpage (the page’s link is provided beneath). On some occasions, a SERP will contain both a knowledge panel and a featured snippet.
Beyond zero-click searches, organic listings must also compete with the following:
- Paid Ads: Paid advertisements were originally relegated to the sidebar. When they snagged position 0, they were the first to push organic listings out of their top spot. Hoping to learn more about the types of advertisements available on Google? Check out our Google Ads page.
- Local Services Ads: Local Services ads (previously known as Google Home Services), are ads for local businesses vetted by Google. These are only available for companies in certain industries – including plumbers, electricians, movers, handymen, locksmiths, and auto service technicians, amongst others – and they’re listed in card form, not as traditional ad text.
- Local Search Listings: When a user searches for anything with a local bent, a local pack will appear. Complete with a map, local listings push organic results even further down the page.
Other SERP features competing for space include image packs, knowledge cards, news boxes, related questions, reviews, shopping results, tweets, and more. Check out a full list of SERP features on Moz.com.
All of this to say, SERPs are more competitive than ever and if you’re relying entirely on organic traffic, always pining for that coveted #1 position on the results page, keep in mind that the organic #1 position is now often bumped down by advertisements, maps, featured snippets, knowledge panels, and videos. By making use of on-SERP SEO, you can optimize for all of a SERP, not just the organic listings.
What Is On-SERP SEO?
On-SERP SEO is the process of optimizing a webpage with the goal of taking up as much real estate on SERPs as possible to increase your click-through rate (CTR) and generate more organic traffic. In the past, meta descriptions and meta titles were the only SERP content that marketers could control. Now, there are more methods available for optimizing your on-SERP presence.
How to Use On-SERP SEO
Review Click Potential
Start looking at CTR as you conduct keyword research and make decisions. Ahrefs makes this simple. Simply type in your search term and view the total search volume, which will be divided into “with clicks” and “without clicks.” If the vast majority of your coveted keyword’s search volume comes up as “without clicks,” you can clearly see the value in on-SERP SEO. Here’s an example:
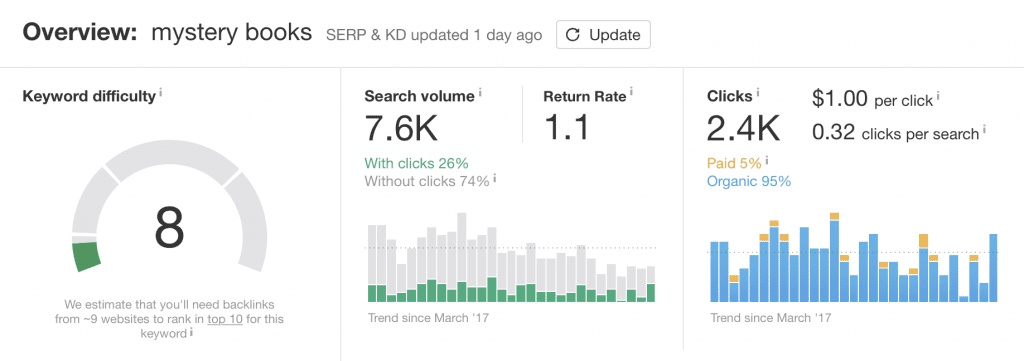
Nearly three-quarters of all searches for “mystery books” never receive a single click! So instead of basing your target keywords on monthly search volume alone, be sure to review click potential as well.
Optimize to Win Featured Snippets
Although securing a featured snippet is not an exact science, there are several things you can do that will likely increase your chances:
- Find Your Targets: Looking at your organic rankings, determine which of your keywords already displays a featured snippet. (Hint: Long-tail queries and question queries often produce featured snippets.) These will give you keywords to target. Also, make a note of which type of featured snippet is included (text, a list, a table, a video).
- Rank Highly: We know that Google usually pulls content from the top 10 rankings of a keyword to fill the featured snippet. So if you want a featured snippet, you first need to focus on traditional SEO to rank highly on the first page of the SERP.
- Understand Your Goal: The purpose of a featured snippet is to directly answer the user’s query so that no clicking is required. You need to accomplish this on the page.
- Write a Precise Answer: Add the keyword or question to the content of your page as a subheading. Then, immediately beneath that, write a brief and precise answer. Match the type of featured snippet already present: text (write a 40-50 word paragraph), a list, a table, etc.
Optimize to Secure Google Sitelinks
Sitelinks increase the real estate of your search listing, displaying the most important pages of your website directly underneath the listing. This is how Google explains their formation: “Our systems analyze the link structure of your site to find shortcuts that will save users time and allow them to quickly find the information they’re searching for . . . We only show sitelinks for results when we think they’ll be useful to the user.”
If you want to optimize for sitelinks, check that the structure of your site allows Google’s algorithm to find good sitelinks. Create a clear navigational structure, adding strong internal links to your site’s core pages. For internal links, always use anchor text and alt text that is informative, concise, and not repetitive.
Add Schema Markup
Sometimes Google’s algorithm struggles to make sense of a page and its content. Using schema markup, you can help bridge the gap. Review the various types of schema markup on Schema.org and then use them within your website. For example, you may wish to add review schema markup, which allows the search engine to display a star rating within your organic search listing. This might improve a user’s opinion of your site’s reputability and lead them to click through. Or you may wish to check out Moz’s guide to schema markup.
Make Good Use of Google My Business
If you aren’t signed up for Google My Business, you’re seriously missing out. This is a great way to target branded searches (queries that include your business’s name), appear in Google Maps, and show up in the local 3-pack. To start, sign up and verify your listing. Then, fill out all of the relevant fields to the best of your ability. Include photos, ask your customers to leave you reviews, list all of your features and amenities, add questions and answers to your listing – go above and beyond to take full advantage of this free feature.
Optimize Your Images
If your target keywords include images in their SERPs, you need to ensure you have images ready to snag those spots. Include an image on the page you’ve built for a particular target keyword, and make sure that image is optimized: write a keyword-optimized file name and alt tag, place your image near relevant text, and size it to a common dimension.
Purchase Google Ads
If you’re worried about the advertisements appearing above the organic listings, why not consider purchasing some ads yourself? With all Google Ads, you will only pay when someone clicks on your ad (which is why these ads are often called pay-per-click, or PPC) or calls your business. You decide when and where your ads appear, so you can target the keywords that matter most to you. You can also set a budget that works for your business and create a monthly cap to ensure you don’t overspend.
It’s especially important to buy branded PPC ads, which target users searching for you. When a user searches specifically for your brand name, there is a high likelihood they’ll convert. Don’t let Google or some other website push you away from the #1 spot on the SERP, potentially stealing your valuable customer. Always have a basic ad campaign targeting your brand name.
_____
Using these techniques, you can seize some of that precious SERP real estate. If you need help getting started, check out 417 Marketing. Our team of knowledgeable, creative, and passionate professionals specializes in SEO, web design and maintenance, and Google Ads, and we have successfully completed over 700 websites since our inception in 2010. Click here to contact us and learn more about what we can do for your company.


